Topics Covered in this article:
Why do you need Micro Segmentation?
Security is one of the prime focus in corporate world. Significant effort, time and money are spent on security of peripheral to End points. These are very effective to block attack at the entry points itself. But, once an end point or server is compromised inside network, peripheral or perimeter security cannot help. All new types of attacks comes everyday and by the time remedies on end points are developed, the threat or the infection spreads within intranet. Containing the compromised asset until the threats are removed, is very important.
Systems are attacked exploiting known vulnerabilities. Often, unnecessary applications, open ports increases the attack surface - that is more opportunities for the attacker. While this should be minimized, but still does not happen most of the time
Micro Segmentation can fill the gap as one of the very effective way to contain compromised asset.
Traditional Networks
In traditional Network, security is set at the edge or periphery, where North-south communication takes place. This secures the intranet or office Network from outside world. Security are extended by creating branches (and sub-branches) and keeping them behind firewall. Communications with outside branch entities has to pass through the firewall at edge of the branch.
This allows unrestricted communication between themselves within the branch. Inter-branch or out side communications from any host in the branch has to go through branch or departmental firewall. Granularity depends on the how many firewalls can be afforded or how many logical firewalls can be created. In all these cases, traffic has to go all the way to the firewall and return to the intended branch. This unnecessarily increases traffic and delays within.
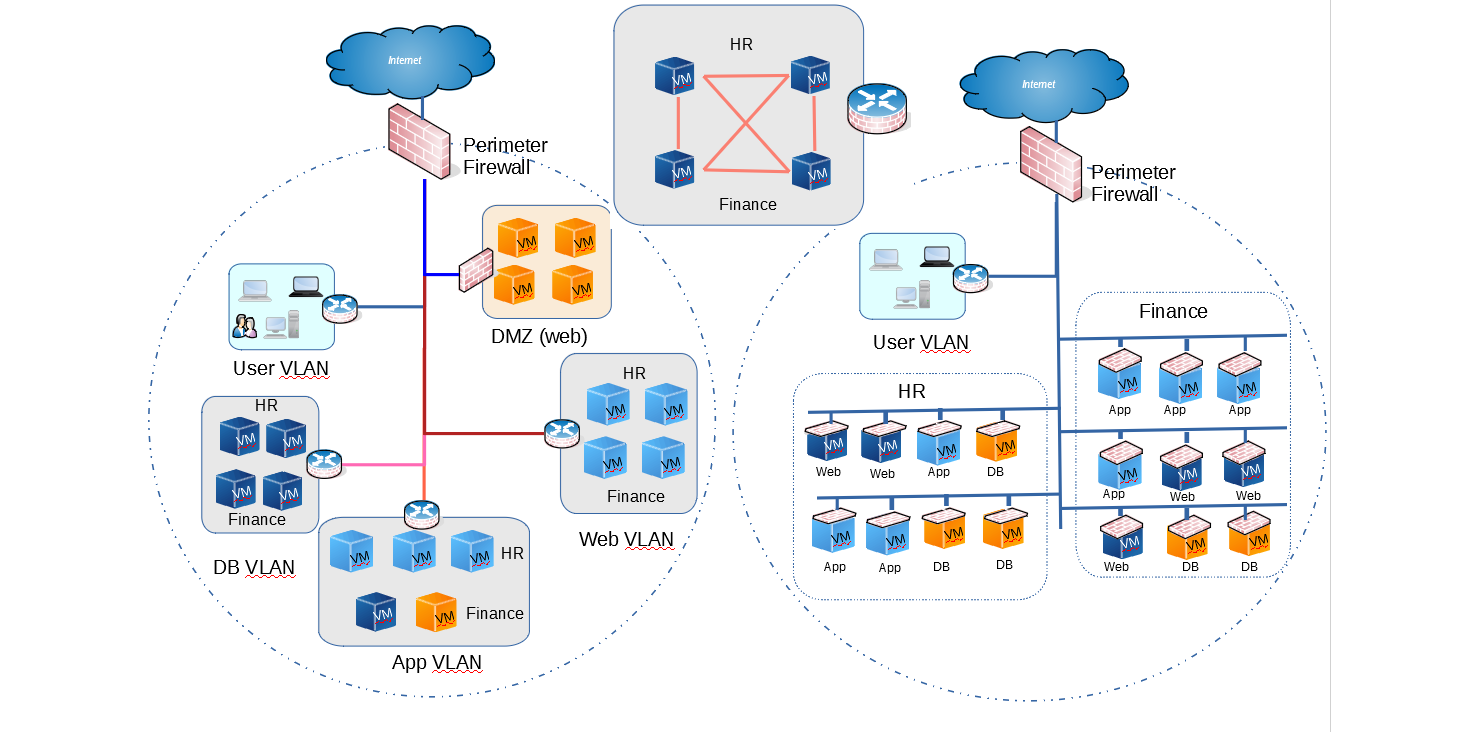
Practically, in most cases the firewall only exists at the edge to connect to outside world or used for creating DMZs, unless, there is some specific needs. An example Traditional network looks like the following
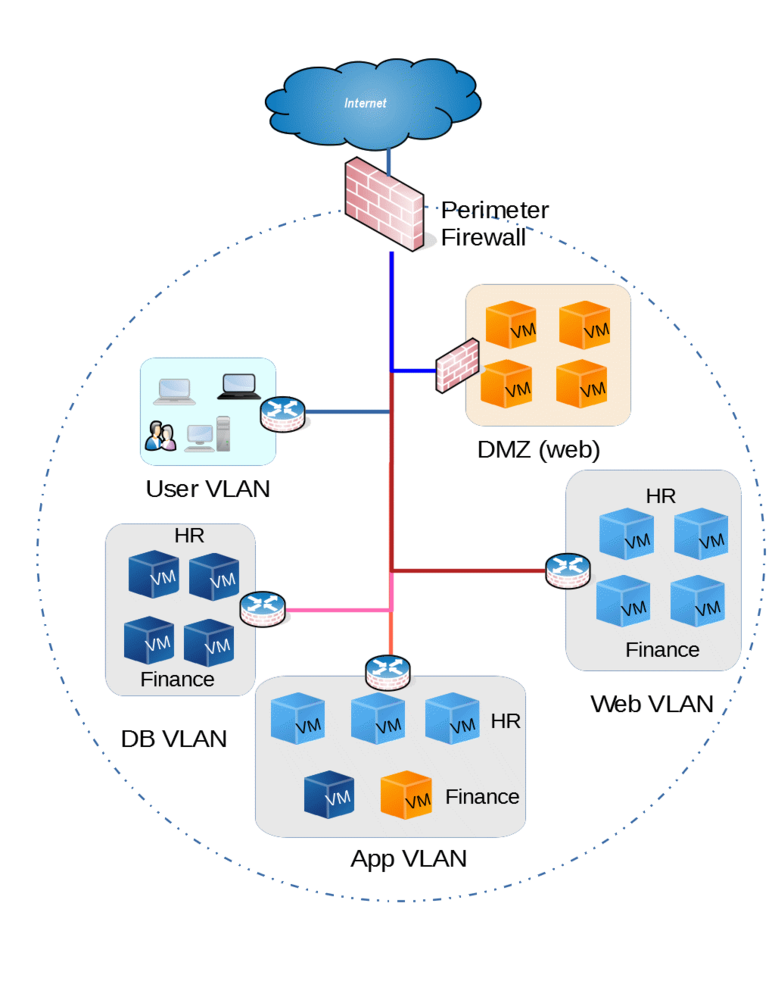
Figure 1 - Traditional Network
The picture below shows that the end points are able to communicate to each other freely within VLANs or subnets behind a firewall. Practically, endpoint count may be in hundreds. Infections in one of these servers are not contained within itself and can easily spread
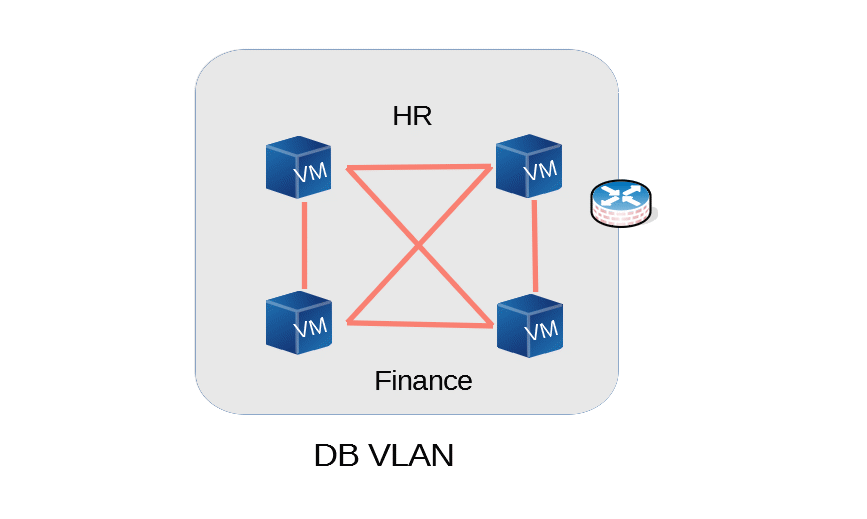
Figure 2. Cross-Talk within branch
What is Micro Segmentation?
Micro segmentation is bringing segmentation or network security at the level of endpoints or workloads. This is virtually having firewalls connected to every virtual machines. This brings granular control on all source and destination traffic right at the workloads. This also enables to implement Zero-Trust Security policy very effectively at the endpoint level. Block all to-and-fro traffic at the end point, as we do not trust anyone and then selectively allow, whats needed.
Because of the nature of granularity, this cannot be achieved with physical Firewalls. When this is done right at the virtualization level or by Virtualization Vendor, this brings more and more controls that can be implemented and can take it to a whole new level. This will make it truly software defined security controls
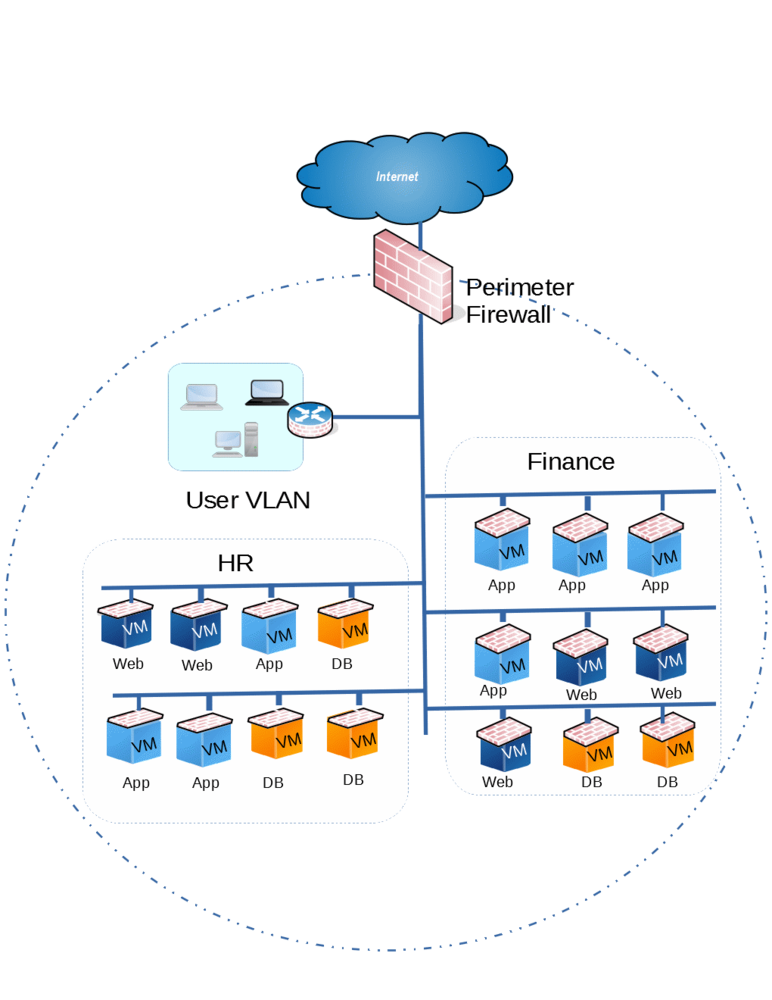
Figure 3. Each endpoint is protected by a virtual Firewall
Micro Segmentation Basics with NSX
Micro-segmentation is segmenting workloads at very granular levels. It is more from the network point of view, so that all source and destination traffic controlled. But modern micro segmentation gives more control than only network. These can extend to application workload or individual person level. It may be able to control who can connect to an application running on a VM from another VM defined through policies that are part of micro segmentation. These are all possible when data center is virtual and most of it is software defined, specially the Network. All the controls are policy based so that policies are defined and workloads are applied with the policies.
We will try to explore this further with VMware NSX. All networking components in NSX are Software Defined, which means these can be configured through management pane as well as through APIs. The main component that is used for micro segmentation is Distributed Firewall. This NSX component is implemented at hypervisor kernel layer giving it full visibility of the in-memory data and traffic in Software defined Network. Traffic is filtered at at the vNIC of each VMs making it impossible to bypass Distributed Firewall.
When NSX is implemented, Distributed Firewall is deployed to each hypervisor as kernel module . This enables distributed enforcement of policy rules configured centrally. The Distributed Firewall can filter traffic at L2 to L4 level. This means security rules can be applied even when the VMs are connected to the same Logical or Virtual switch, irrespective of their IP subnet or VLAN.
The filtering of traffic happens happens based on series of security (policy) rules. The last one obviously to DENY All. Policies are applied top to bottom and stops after executing the match. The source and destination in the rules can be Security Groups in addition to traditional IP and Ports. Security Groups are defined using anything from VMware vSphere inventory. This may include
- Static values
- Tenant or department name
- Logical Switch or VDS name
- Operating system ( even like OS name containing "Windows")
- VM name
- Security tags (This can be added to VMs dynamically or statically)
- any other entity within VMware vSphere inventory
Service composer is another advance topic, where this merges with other providers for Antivirus etc. and security groups can include user identity and security posture. This may be used to dynamically quarantine infected endpoint or VM.
Benefits of Micro Segmentation
Security - This is the prime driver for Micro-segmentation
Speed - Since micro-segmentation is implemented at Virtualization layer, mostly the configuration are centralized. Configurations can be made effective without down time. Security Policies can be based on dynamic state and in those cases, based on the state of endpoint changed might be instantaneous. With support of APIs this can be done in self-service consumption mode
Granularity - This give tremendous level of granularity. With proper vendor echo-system, this can be extended to introspect for security posture and certain action including quarantine of endpoints
Policy based - Extended rules possible using security groups, security tags. It makes it truly software defined
Zero Trust - Trust level can be narrowed down as very granular level of control is possible. Allow only the intended traffic
Performance - Since, the the firewall features are kernel modules, it uses of modern days compute power and can process quite large number of rules without affecting performance. Further, it reduces hair pinning. Traffic do not need to leave the Virtualization host, if the the destination in within the same host. It can reduce traffic and limit to the TOR Switch when destination is in the same rack